AND, OR, NOT
The WHERE clause can be combined with AND, OR, and NOT operators.
The AND and OR operators are used to filter records based on more than one condition:
The AND operator displays a record if all the conditions separated by AND is TRUE.
The OR operator displays a record if any of the conditions separated by OR is TRUE.
The NOT operator displays a record if the condition(s) is NOT TRUE.

LIKE
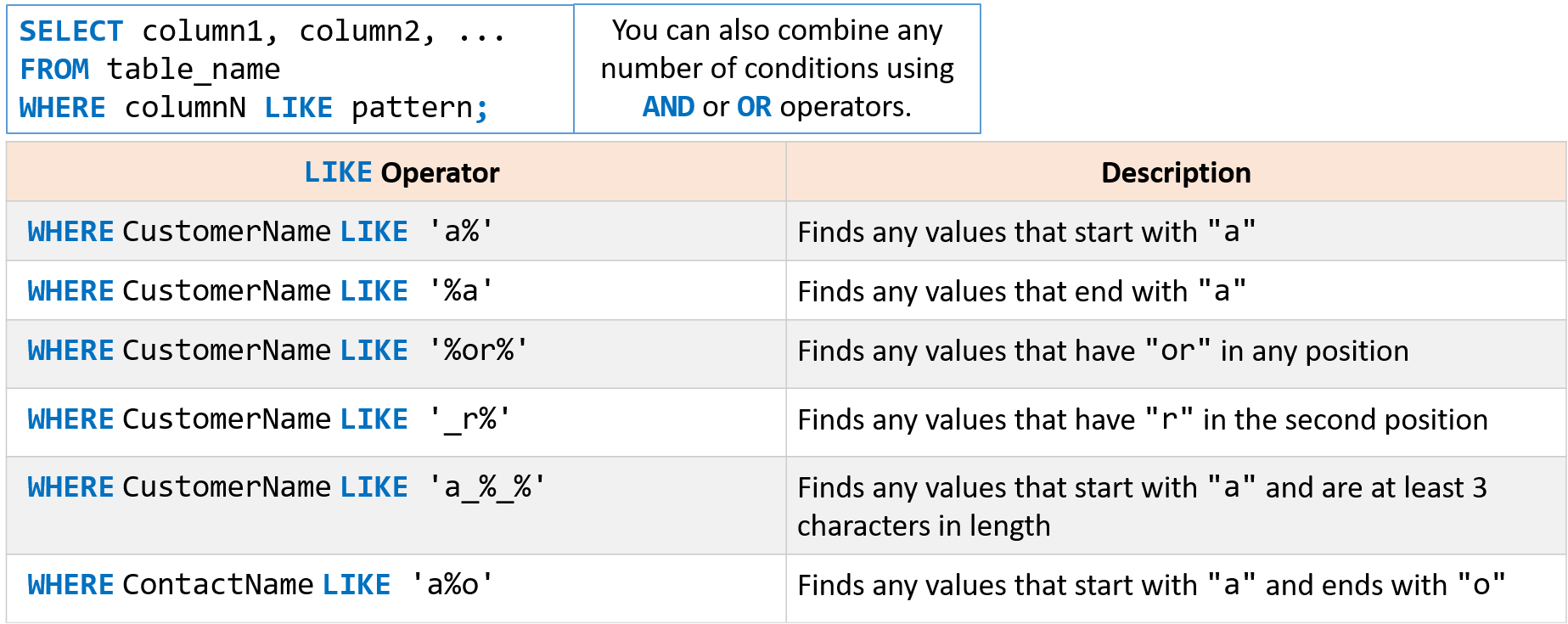
The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
There are two wildcards used in conjunction with the LIKE operator:
% the percent sign represents zero, one, or multiple characters.
_ the underscore represents a single character.
And of course the wildcards can be used in combination with one another.
Wildcard characters
A wildcard character is used to substitute any other character(s) in a string.
Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator.
The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
There are two wildcards used in conjunction with the LIKE operator:
- `% the percent sign represents zero, one, or multiple characters.
_the underscore represents a single character.
And of course the wildcards can be used in combination with one another.

IN
The IN operator allows you to specify multiple values in WHERE clause.
The IN operator is shorthand for multiple OR conditions.

BETWEEN
The BETWEEN operator selects values within a given range.
The values can be numbers, text, or dates.
The BETWEEN operator is inclusive: beginning and end values are included.

NULL NOT NULL
A field with a NULL value is a field with no value.
If a field in a table is optional, it is possible to insert a new record or update a record without adding a value to this field.
In which case, the field will be saved with a NULL value.
Testing for NULL values
- It is not possible to test for
NULLvalues using comparison operators (=, <, <>) - Instead, you have to use the
IS NULLandIS NOT NULLoperators.

ORDER BY
The ORDER BY keyword is used to sort the result-set in ascending or descending order.
It sorts the records in ascending order by default.
To sort the records in descending order, use the DESC keyword.

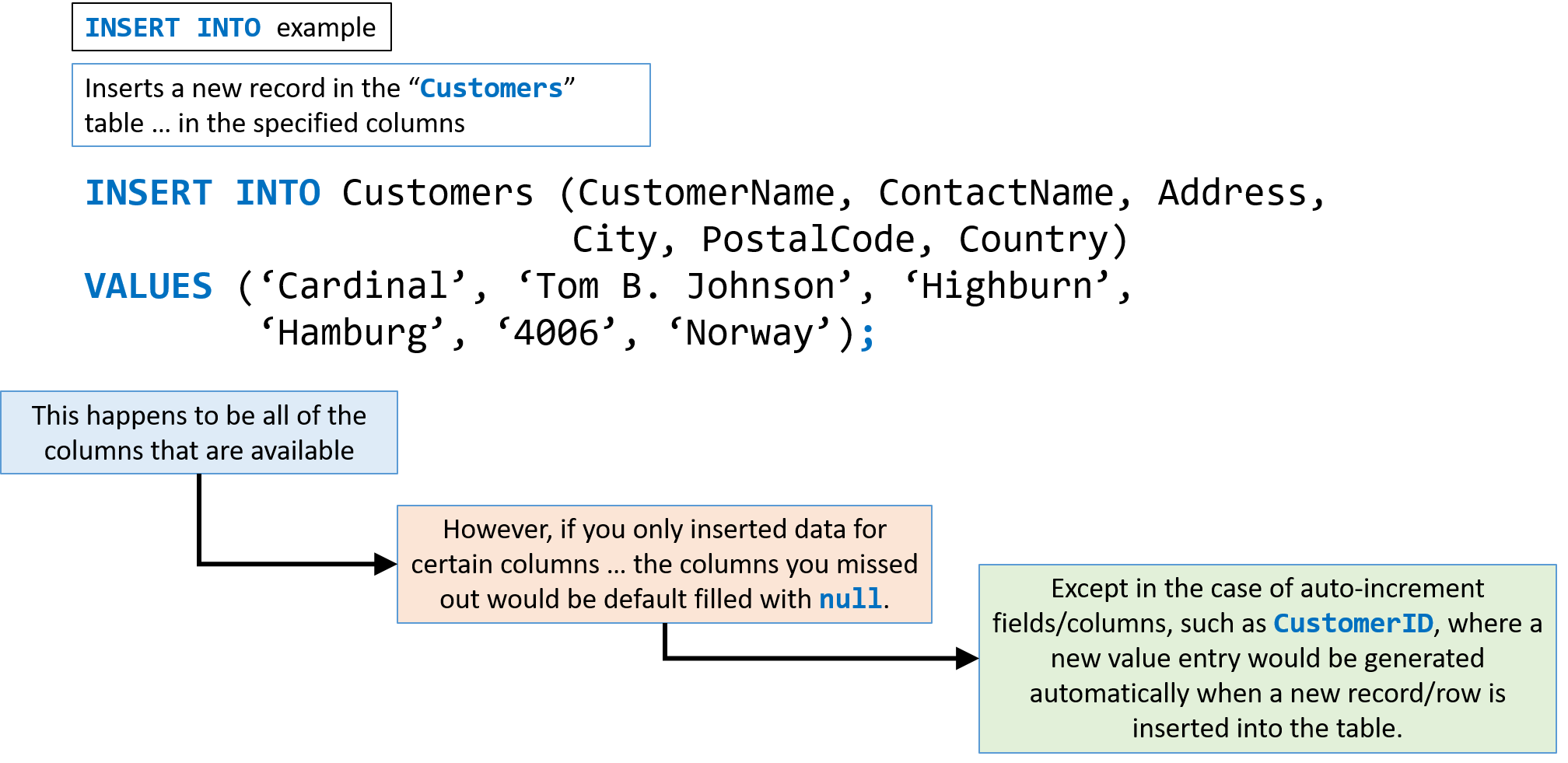
INSERT INTO
The INSERT INTO statement is used to insert new records into a table.
It is possible to use the INSERT INTO statement in two ways:
-
The first way specifies both the column names and the values to be inserted:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, …) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, …);</code><br/> -
If you are adding values for all the columns of the table, you do not need to specify the column names in the SQL query. However, make sure the order of the values is in the same order as the columns in the table:
INSERT INTO table_name
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, …);